The spasticity app for your health – Life after a stroke – our latest video
The Spasticity App
This spasticity app was developed by doctors and specialists to help patients after a stroke to detect the early development of spasticity. Note: For reasons of better readability, the male form is used for personal names. In the interests of equal treatment, corresponding terms generally apply to all genders. The shortened form of language is for editorial reasons only and does not imply any evaluation.
Developed and recommended by doctors
Prof. Dr. med. Siegfried Jedamzik, first chairman of the regional practice network GOIN eV and managing director of Bayerische TelemedAllianz GmbH, developed the spasticity app with the support of Dr. med. Dipl.-Psych. Friedemann Müller, head physician of neurological early rehabilitation & rehabilitation at the Schön Klinik Bad Aibling Harthausen.
Dr. med. Dipl.-Psych. Friedemann Müller
Buttonstroke
What is a stroke? A stroke is the "sudden" loss of certain functions of the brain. This can occur for various reasons. One example is a blood clot blocking a blood vessel in the brain.
Hemorrhagic stroke

What is a hemorrhagic stroke (brain hemorrhage)?
In a hemorrhagic stroke, an artery in the brain ruptures or bursts (see image). The nerve cells are damaged due to the space-occupying bleeding.
Ischemic stroke
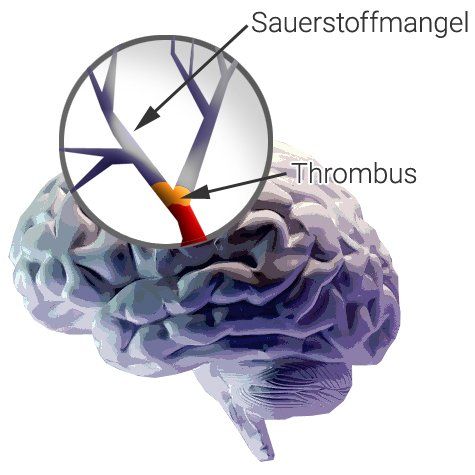
What is an ischemic stroke (cerebral infarction)?
In an ischemic stroke, a blood clot (thrombus) blocks an artery in the brain (see image). This interrupts the blood supply to this artery and the brain cells are no longer supplied with oxygen and nutrients.
The spasticity app for your health!
❤️📱 Get the free spasticity app after a stroke now and receive valuable recommendations for action!
Use the spasticity app after a stroke
Download for free. Document important information. Receive important recommendations for action.
Spasticity app for the time after a stroke!
This valuable application offers you helpful recommendations for action should spasticity develop.
📱 The app is available in a total of 9 different languages so that you can get the best information in your native language. Your health is our top priority! 🧡
Get the Spasticity app now for free from the App Store and Google Play Store. Together we will overcome every challenge on your road to recovery! 💪
This is how you recognize a stroke! | AOK - The health channel
What: YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Do3UJBNzirc
What is spasticity?A pathological increase in muscle tension caused by damage to the central nervous system.When does spasticity occur?
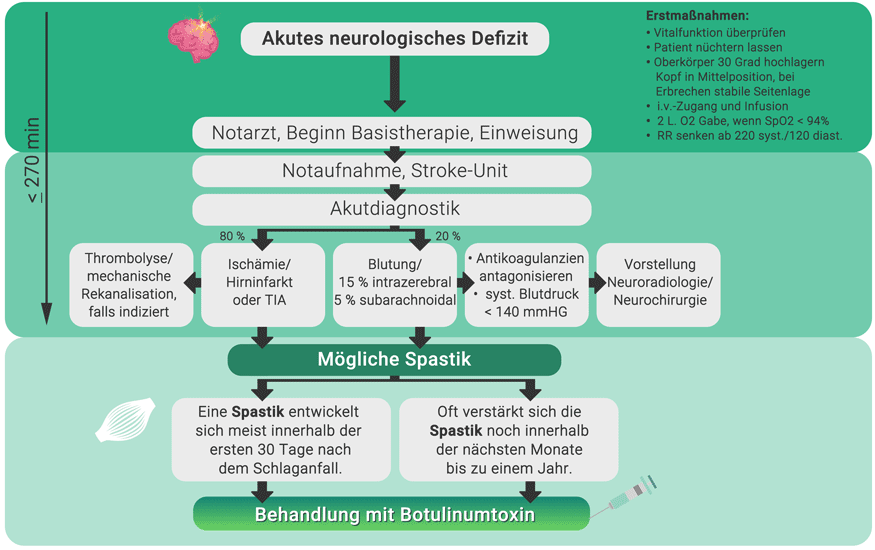
Spasticity usually develops within the first 30 days after the stroke in around a quarter of those affected. The spasticity often gets worse over the next few months to a year.Did you know that spasticity can be treated with botulinum toxin?The drug botulinum toxin type A is extracted and processed under strict conditions from the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. The effect of botulinum toxin type A is so extreme that just a few billionths of a gram are enough to relieve cramps. This is why botulinum toxin is a treatment method for spasticity. How does botulinum toxin work?After the injection of botulinum toxin, the spasticity improves within a few days.The effect of the treatment reaches its peak within a few weeks and normally lasts three to four months. The therapy must be repeated at regular intervals because the effect of botulinum toxin between the nerves and muscles is only temporary and the active ingredient is broken down by the body.
Video
Patients before and after treatment with botulinum toxin. Improvement of gait stability and reduction of the risk of falls through botulinum toxin type A in spastic-dystonic supinated-inverted equinus after stroke.
Source: Dr. med. Martin Schorl, Chief Physician of the Neurological Clinic at the Bad Wurzach Rehabilitation Clinic.
Guidelines
"In focal spasticity, focal drug injection treatment with botulinum toxin A (BoNT A) usually has a better benefit-risk ratio (see below) and should, where possible, be used before the use of oral antispastics (strong consensus)." (See source: Guidelines for diagnostics and therapy in neurology, p. 8)Source: AWMF online: Guidelines for diagnostics and therapy in neurology. Therapy of spastic syndrome. German Society of Neurology, p. 8Long version: https://register.awmf.org/assets/guidelines/030-078l_S2k_Therapie_spastic_Syndrom_2019-06-verlaengert.pdf














